How does cannabis work in our bodies? What is the Endocannabinoid System?
Written by Kelly McLoughlin & Britt Foster
The endogenous endocannabinoid system, or ECS, is a vast signaling and receptor system within the body. It helps with overall function. Discovered by scientists in the 1990’s, research is still being conducted and more is being learned every day. According to UCLA, the endocannabinoid system evolved over 500 million years ago and is present in all vertebrates. All mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibians, and even fish have ECS’s!
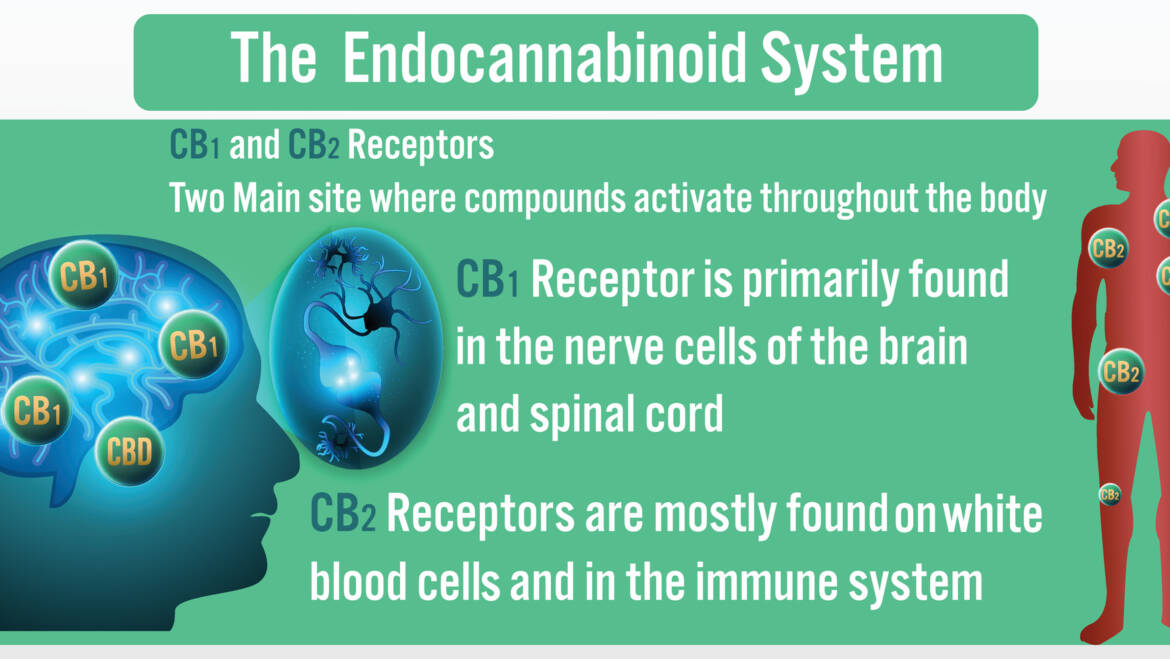
In humans, this receptor system is just about everywhere in your body. It’s in the brain, the immune system, most of the major organs, the lymph system, the digestive system, and the spine.
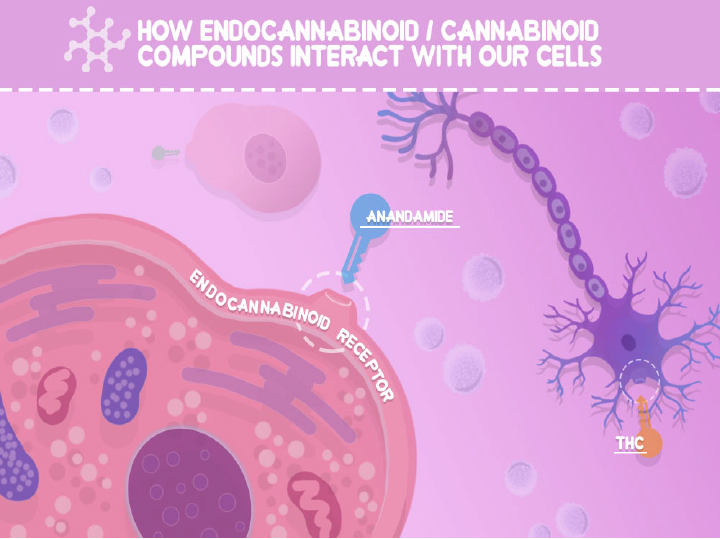
The purpose of your endocannabinoid system is to create and maintain balance (homeostasis) in your body. This means that when a function of your body is overactive or underactive, your endocannabinoid system is supposed to bring you back into a state of balance. It does this by creating endocannabinoids, which are signaling molecules that interact with our cells.
Your body produces endocannabinoids naturally. “Endo-” means internal. When you’re totally healthy, your body is theoretically producing enough endocannabinoids to keep your system in balance. This ensures that you sleep well, have a healthy appetite, feel good, etc.
Modern Chronic Stress
There are many aspects of today’s world that deplete the endocannabinoid system. Chronic stress, poor diet, environmental toxins, and a sedentary lifestyle all have a negative impact. The human body is incredible at adapting to environmental changes, but the last several centuries have seen a dramatic shift away from what is biologically natural. We eat processed foods packed full of chemicals and gorge ourselves on sugar. We sit in chairs all day in stuffy enclosures. Long work hours wear us out, endless screen time puts us in a daze, and doctors throw pills at us instead of tending to the root cause. The human body cannot evolve fast enough to handle all these man-made environmental changes.
When the endocannabinoid system can’t keep up with the chronic stress and toxic world we live in, it becomes depleted. If it’s depleted, it cannot maintain proper homeostasis in the body. When the body lacks homeostasis, disease happens.
Some of the diseases associated with this include autoimmune diseases, epilepsy, migraine headaches, fibromyalgia, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and depression.
So the question is, how do we fix it?
Endocannabinoids vs. Phytocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are both cannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are produced by the body, and phytocannabinoids are made by plants. Phytocannabinoids are therefore exogenous, which means they are produced outside the body.
Both endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
The endocannabinoid system is full of receptor sites called CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors exist mainly in the central nervous system, and CB2 receptors are mostly associated with the immune system. Cannabinoids attach to these receptors and regulate the body’s production of other neurotransmitters. This affects the whole body.
In the neuroscience journal “Cerebrum”, author Bradley E. Alger writes, “given the enormous complexity of the brain, the endocannabinoid system could affect behavior in an almost limitless number of ways” (2013).
Neurotransmitters and the Endocannabinoid System
An easy way to visualize the interaction of cannabinoids and receptors is like a lock and key. The receptors are the locks and the cannabinoids are the keys. When the right key goes into the right lock, the receptor reacts and triggers a change. It can inhibit as well as encourage the release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body uses to send signals between the cells. Although cannabinoids are not technically neurotransmitters, they work in a similar way.
Neurotransmitters play a part in just about every aspect of your body’s functioning. They are involved in learning, memory, mood, motor control, sleep, attention, and just about everything else. You can think of neurotransmitters as the essential messengers that keep your body running, and the endocannabinoid system as the “traffic police” that makes sure the messengers are behaving correctly.
Pain Relief, Better Sleep, and More
If your body is not producing enough of its own endocannabinoids, you can supplement with phytocannabinoids. The best source is the cannabis plant. There are dozens of cannabinoids in a cannabis plant, but the most popular ones are THC, CBD, and CBG. Each cannabinoid interacts with the ECS in its own way.
Both CBD and CBG help replenish the endocannabinoid system. When the plant compound goes into your body, it attaches to the CB1 or CB2 receptors and triggers a change to help restore balance. This is why we are seeing cannabis help with absolutely everything. It works in harmony with your body by strengthening the system that maintains balance.
The key word here is balance. The endocannabinoid system is basically everywhere except the brainstem, which controls breathing. Therefore, it’s impossible to lethally overdose on cannabis. It is still important, however, to maintain a balanced relationship with cannabinoids. THC, for example, can have a negative impact after excessive, long-term use.
You don’t want to flood your endocannabinoid system, you just want to keep it replenished.
CBD and CBG are popular because they do not have any intoxicating effects. Both work in similar ways and help with many of the same conditions. The most effective way to replenish your endocannabinoid system is to take a full-spectrum, whole-plant CBD or CBG tincture. Full spectrum means that the tincture contains small traces of all the plant’s natural cannabinoids. With CBD tinctures, it means that although the product is mostly CBD, there is also a small amount of THC. This ratio is natural to the plant and seems to be the most effective.
Conclusion
You have this vast receptor system that exists almost everywhere in your body. This system maintains homeostasis. If your body goes out of whack, your endocannabinoid system helps restore balance. When your body is not producing enough of its own cannabinoids, you can supplement with an external source. Phytocannabinoids from cannabis work great and help you return to a happy and healthy self.
What if cannabinoids are actually the key to health and happiness? Humans evolved with plants. We take echinacea for colds, St. John’s Wort for depression, chamomile for calming, and so on. It’s time to take a closer look at cannabis and be open to the positive impact it can have.
→SHOP FLOWERCHILD PRODUCTS NOW←
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult your doctor before using any new supplements.